Decoding CPU Names: Understanding AMD & Intel's Nomenclature
Who Is This Article For?
Beginners: This article offers basic guidance in simple terms for those new to PCs.
Computer technology is always changing. CPU names can be confusing with their mix of numbers and letters. This article explains these names. We focus on AMD and Intel, two big names in the industry. We'll show you how they name their CPUs.
Every part of a CPU's name tells us something important. This includes things like core counts and generation. We'll explain what these names mean. This will help you understand a CPU's power and abilities.
This guide is for anyone interested in technology. It's for professionals, tech fans, and anyone curious. We'll help you make smart choices in the fast-paced world of computers.
Breaking Down Intel's CPU Naming Structure
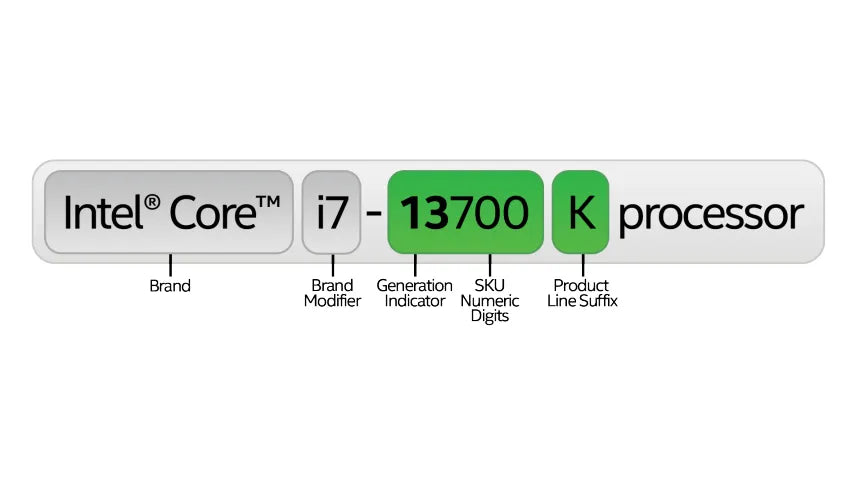
Brand
Intel's processor names start with the brand. This is the product line the processor belongs to. Most Intel processors are named Intel Core. There's also a new name – “Intel Processor”. This new name replaces Intel Pentium and Intel Celeron starting in 2023.
Intel Processor is for budget-minded buyers. It's more affordable. Intel Core processors are faster. They have extra features not in Intel Processor models.
Intel Xeon processors are for top performance. They're used in servers and workstations. They're more powerful than other Intel processors.
Brand Modifier
Core i9
Since its debut in 2017, Intel's Core i9 has been at the forefront of the consumer processor market. The 13th gen Core i9 models, codenamed Raptor Lake, are equipped with 36 megabytes of cache and a total of 24 cores. This configuration includes eight multi-threaded high-performance cores for CPU-intensive activities and 16 more energy-efficient cores for less demanding tasks. Featuring Turbo Boost Max 3.0, these processors can identify and utilize the fastest cores for additional speed, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks like 3D rendering or video editing.
Core i7
Next, we have the Core i7, which offers similar capabilities but in a slightly scaled-down version. It has the same eight high-performance cores as the Core i9 but only eight efficiency cores, totaling 16 cores. The cache size is reduced to 30 megabytes, yet it still includes Turbo Boost Max 3.0. The Core i7 is a solid choice for streamers or content creators who need substantial power but not quite to the extent of the Core i9.
Core i5
The Core i5 sits comfortably as the go-to option for many users. It features six high-performance cores and either four or eight efficiency cores, depending on the specific model. Although the cache is smaller, at 24 or 20 megabytes, and lacks Turbo Boost Max 3.0, the price reduction makes it a compelling option. It's particularly suitable for gaming PCs, offering a great balance between performance and cost.
Core i3
Moving further down, the Core i3 offers a more basic setup with four high-performance cores and 12 megabytes of cache. It's adequate for light to moderate gaming and can handle AAA titles that require more than six cores, albeit with potential limitations. Its much lower price point makes it an attractive choice for those who don't need excessive power but still want efficient multitasking capabilities.
Generation Indicator
It follows the brand and brand modifier. For most Intel® Core™ processors, the generation is in the processor number. It's right after the dash. If a processor number has four or five digits, the first one or two digits show the generation. For example, a processor numbered 9700 is from the 9th Generation. One labeled 12800 is a 12th Generation processor. This helps you know how new or old a processor is.
SKU Numeric Digits
The last part of Intel® processor names are SKU numeric digits. These are the final three digits of the product number. SKUs show the order of development within a generation and product line. Usually, a higher SKU means more features in similar processor brands and generations.
But be careful. SKU numbers aren't great for comparing different generations or product lines. They are best used to compare processors within the same generation and brand. This helps understand the variety within a specific Intel® processor range.
Product Line Suffix
The SKU suffix in Intel® processor names shows their specific capabilities. It's a letter-based product line suffix. For instance, in the Intel® Core™ series, 'U' means the processor is for power-efficient laptops or 2-in-1s. 'XE' stands for "extreme edition." This is for desktops built for top performance.
Each suffix gives a quick idea of what the processor is best for. It helps to understand the intended use of each processor. This is especially useful when choosing the right processor for your needs.
Processor Suffixes
To understand what a processor suffix indicates, consult the list below. Not all processor generations or families include all product suffixes.
|
Form/Function Type/Segment |
Suffix |
Optimized/Designed For |
|
Desktop |
K |
High performance, unlocked |
|
F |
Requires discrete graphics |
|
|
S |
Special edition |
|
|
T |
Power-optimized lifestyle |
|
|
X/XE |
Highest performance, unlocked |
|
|
Mobile (Laptop2, 2 in 1) |
HX |
Highest performance, all SKUs unlocked |
|
HK |
High performance, unlocked |
|
|
H |
High performance |
|
|
P |
Performance for thin & light |
|
|
U |
Power efficient |
|
|
Y |
Extremely low-power efficient |
|
|
G1-G7 |
Graphics level (processors with newer integrated graphics technology) |
|
|
Embedded |
E |
Embedded |
|
UE |
Power efficient |
|
|
HE |
High performance |
|
|
UL |
Power efficient, in LGA package |
|
|
HL |
High performance, in LGA package |
Deciphering AMD's Processor Names
AMD's processor nomenclature can be a bit complex, but understanding it is key to identifying the right processor for your needs. Let's break down the naming conventions for the different AMD brands, including Ryzen, Athlon, EPYC, and Threadripper, and explain the significance of the "X" and "X3D" suffixes.
AMD Brands
Ryzen: This is AMD's primary brand for consumer CPUs. Ryzen processors are known for their high performance and are popular among gamers, content creators, and general consumers. They come in several categories: Ryzen 3, Ryzen 5, Ryzen 7, and Ryzen 9.
- Ryzen 3: Entry-level CPUs, suitable for basic computing tasks.
- Ryzen 5: Mid-range CPUs, offering a balance of performance and price, ideal for moderate gaming and content creation.
- Ryzen 7: High-end CPUs, designed for demanding applications and multitasking.
- Ryzen 9: Top-of-the-line CPUs, offering the best performance for intensive gaming, content creation, and other demanding tasks.
Athlon: These are budget-friendly CPUs designed for everyday computing tasks. Athlon processors are generally less powerful than Ryzen CPUs but are a good choice for basic tasks like web browsing, office applications, and light media consumption.
EPYC: AMD's EPYC series is targeted at the server and enterprise market. These processors offer high core and thread counts, robust security features, and are designed to handle heavy workloads like data centers, cloud computing, and enterprise applications.
Threadripper: Aimed at the high-end desktop (HEDT) market, Threadripper CPUs offer an even higher core and thread count than Ryzen 9 CPUs. They are ideal for professional content creation, 3D rendering, and other CPU-intensive tasks that benefit from the increased processing power.
AMD's updated naming scheme for their CPUs represents a significant shift, aiming to provide more clarity about the chip's generation and capabilities but also introducing some complexities. Here's a brief analysis of the new versus old naming conventions:
New Naming Convention Four-Digit System with a Letter Suffix
This structure is more detailed, allowing for a more granular understanding of the CPU's generation, performance category, and specific features.
Second Digit (Category Indicator)
The somewhat confusing aspect here is the overlap in categories, where a digit could represent two different Ryzen categories. This could potentially lead to some confusion among consumers.
Third Digit (Architectural Generation)
This is a straightforward and helpful indicator of the chip's technological generation, making it easier to understand the architectural advancements in the CPU.
First Digit (Model Year)
Placing the model year upfront is a double-edged sword. It helps quickly identify the model's year, but it can also make older designs seem more current than they are, potentially misleading consumers.
Fourth Number and Letter Suffix
Differentiating between lower-end and higher-end chips is useful. The suffixes (like HX, HS, U, C, E) are familiar and informative for those acquainted with CPU specifications, indicating the intended use or power level of the CPU.
|
Suffix |
Meaning |
Typical Use |
|
X |
High performance |
Higher clocked CPUs, better overclocking potential |
|
G |
Integrated graphics |
CPUs with AMD Radeon Graphics |
|
U |
Ultra-low power |
Laptops, balance between performance and battery life |
|
H |
High-performance laptops |
Gaming laptops and high-end ultrabooks |
|
S |
Special edition / Variant |
Desktop CPUs, different specifications or TDP |
|
T |
Low power |
Desktop CPUs, lower power consumption and heat output |
|
E |
Embedded |
CPUs designed for embedded systems |
|
WX |
Workstation-class |
High-end CPUs for professional applications |
|
HS |
Slim gaming laptops optimized version of H series |
Slim gaming laptops with lower power consumption |
|
XT |
Enhanced version of X series |
Higher clock speeds, improved overclocking |
|
Pro |
Professional and business applications |
Additional security features, longer warranty/support |
X3D Suffix
In AMD processors, the "X3D" suffix signifies a special feature related to 3D V-Cache technology. Here's a breakdown of what this means:
AMD's 3D V-Cache technology stacks extra cache layers on CPUs, increasing L3 cache size. This boosts performance, especially for gaming and data-heavy tasks. Processors with X3D suffix offer enhanced performance by reducing latency and increasing cache bandwidth. These processors target high-performance users like gamers, content creators, and data-intensive professionals.
Conclusion
Understanding the nomenclature of CPUs by AMD and Intel is vital for making informed decisions in the tech world. Both brands use a mix of numbers and letters to denote specifics like generation, performance category, and features, though their approaches differ.
Intel's naming includes brand, brand modifier, generation indicator, SKU numeric digits, and product line suffix, each revealing essential information about the processor's capabilities.
On the other hand, AMD's updated naming scheme for laptop CPUs, though more complex, offers a detailed understanding of the chip's year, performance category, and technological generation. This detail-oriented approach aligns with Intel’s strategy, reflecting an industry trend towards more informative but intricate naming systems.
Decoding these names is crucial for beginners, tech enthusiasts, or professionals in making the right choice for their needs. Whether you are upgrading your system or building a new one, comprehending these CPU names will empower you to choose components that align perfectly with your computing requirements.
Remember, in the rapidly evolving world of technology, staying informed and understanding the language of the industry is key to navigating its challenges.
Need help picking out the perfect CPU for your new build or upgrade? Visit Prime Tech Support to compare models and get expert advice tailored to your computing needs.
Sources
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lpraYE-TLeM&ab_channel=Techquickie
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/processors/processor-numbers.html
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BEHe7Op6IQ4&ab_channel=HardwareJunkie
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BEHe7Op6IQ4&ab_channel=HardwareJunkie
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oErJG3fThF0&ab_channel=Techquickie
Articles You Might Be Interest In
Best Gaming CPUs in 2023: Top Picks for Elite Performance
How to Choose an SSD for Gaming
PC Crashes While Playing Games: Problem Solved!
SAME-DAY REPAIRS
Gaming PC Diagnostic
Fast tech support for Gaming Computers. We exceed customer expectations and ensure satisfaction.